|
[ Back to index ] 3. Results
3.1 The IBA network in Vietnam
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A total of 63 IBAs were selected in Vietnam; a detailed site account for each is given in Chapter 4. Fifty eight IBAs (92% of the total) qualified under two or more categories, although only one IBA, Ban Thi Xuan Lac (VN029), qualified under all four. Sixty two IBAs (98%) qualified under category A1, emphasising the significance of the IBA network for the |
Table
3: The number of IBAs in each category
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
conservation of globally threatened species. The one IBA that did not qualify under category A1, Sinh Long (VN028), qualified under category A3, due to the presence of a number of biome-restricted species known from few other sites in Vietnam (Table 3). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.2 Coverage of the IBA network
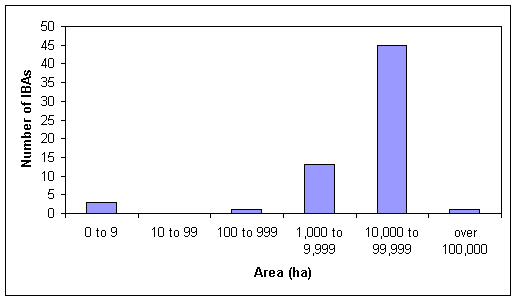
Size. The 63 IBAs in Vietnam cover a total area of 1,689,866 ha, equivalent to 5% of the total land area of the country. Vietnam's IBAs range in size from 2 to over 100,000 ha, although most are in the range from 10,000 to 99,999 ha. The mean IBA size is 26,823 ha, while the median size is 22,200 ha. The relative lack of very large IBAs in Vietnam (only 10 IBAs are larger than 50,000 ha and only one is larger than 100,000 ha) reflects several factors, including the fragmented nature of natural habitats in the country and the selection criterion that, wherever possible, IBAs should be areas that can be managed as a single unit. The relative lack of small IBAs (only four IBAs are smaller than 1,000 ha) reflects the selection criterion that IBAs should be self-sufficient areas, which provide all the requirements for the birds they are important for during the time they are present. All four IBAs smaller than 1,000 ha are bird sanctuaries in the Mekong Delta (Figure 1). Figure
1: Distribution of IBAs by size class
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provinces. IBAs were selected in 37 of Vietnam's 61 provinces and cities (Map 1). The provinces containing the greatest number of IBAs are Dak Lak, Lam Dong, Gia Lai and Quang Binh. Together, these four provinces contain 19 IBAs (30%) (Table 4). These provinces should, therefore, be considered high priorities for conservation action. It is notable that three of the four provinces with the highest number of IBAs are located in the Central Highlands, where there are large areas of natural habitat, and three Endemic Bird Areas (EBAs). The fourth province, Quang Binh, is located in the Annamese Lowlands EBA. |
Table
4: The provinces with the highest number of IBAs
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
There remain twenty four provinces and cities in which IBAs have not been selected to date. These provinces and cities are concentrated in the Red River and Mekong Deltas but also include a significant number in north-eastern Vietnam. This distribution reflects partly the relatively limited extent of natural habitats in these regions, and partly the relatively low level of ornithological survey they have received. With further surveys, it may be possible to identify a number of additional IBAs in these regions. Many of these IBAs would be identified in north-eastern Vietnam, where significant areas of unsurveyed natural habitat remain. However, it may also be possible to identify a number of additional IBAs within the heavily populated Red River and Mekong Delta provinces, many of which support bird sanctuaries: waterbird breeding colonies and communal roosts within anthropogenic landscapes, many of which are under informal forms of protection. Habitats. Forty one IBAs (65%) contain examples of terrestrial forest ecosystems. All the major forest habitats in Vietnam are well represented within these IBAs, including lowland evergreen, montane evergreen, semi-evergreen, deciduous, limestone and coniferous forest (Map 3). In addition, these IBAs include some of the most intact remaining examples of riverine forest in Vietnam, such as the Kon river in Kon Cha Rang IBA (VN025) and the Srepok river in Yok Don IBA (VN044). Eight IBAs (13%) are located in freshwater ecosystems. The natural habitats at these IBAs mainly comprise seasonally inundated grasslands, freshwater swamps and Melaleuca forest, although this category also includes three bird sanctuaries, which provide roosting and nesting areas for waterbirds that feed in freshwater wetlands in the wider area. All eight freshwater IBAs are located in the Mekong Delta, and represent some of the most significant remaining examples of the natural ecosystems that once dominated the delta: Tram Chim and Lang Sen IBAs (VN006 and VN007) support the most significant remaining examples of the Plain of Reeds grasslands; Kien Luong and Ha Tien IBAs (VN005 and VN003) support the most significant remaining examples of the Ha Tien plain grasslands; while U Minh Thuong IBA (VN004) supports one of the most significant remaining examples of the U Minh Melaleuca forests. Coastal ecosystems are represented at 14 IBAs (22%). The natural habitats at these IBAs include intertidal mud and sand flats, mangroves and reedbeds. Six of these IBAs are situated in the coastal zone of the Red River Delta, while five are located in the coastal zone of the Mekong Delta. One IBA is located near the mouths of the Dong Nai, Sai Gon and Vam Co rivers, while two are located in the coastal zone of Quang Ninh province, to the north of the Red River Delta. It is notable that the IBA network does not include any sites in the coastal zone of central Vietnam. While this may be partly attributable to disparities in survey effort, the main reason is probably the absence of major estuaries in central Vietnam, and, consequently, the relatively limited area of intertidal habitats suitable for migratory waterbirds. Detailed surveys of coastal lagoons in central Vietnam may, however, reveal a number of IBAs not yet identified. Category A1 species. According to Threatened Birds of Asia1, a total of 72 globally threatened, near-threatened and data deficient bird species occur in Vietnam. Thirty four of these species (47%) are confirmed to regularly occur in significant numbers at at least three IBAs, while 51 species (71%) are confirmed to regularly occur in significant numbers at at least one IBA (Table 5, Appendix 2). Of the 21 species that are not confirmed to regularly occur at any IBA, many are no longer believed to occur in Vietnam as anything other than vagrants, or are passage migrants or rare winter visitors that do not occur in significant numbers at any site. Table
5: Coverage of category A1 species within IBAs
Note:
the figures in the table exclude IBAs where the species is unconfirmed,
or where the species is not confirmed to regularly occur in significant
numbers. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The IBA network in Vietnam includes all sites where globally critical and endangered bird species are confirmed to regularly occur in significant numbers. However, no globally critical species and only three global endangered species are confirmed to occur at at least three IBAs: Spotted Greenshank Tringa guttifer, Black-faced Spoonbill Platalea minor and Collared Laughingthrush Garrulax yersini (Table 6). In addition, both Edwards's Pheasant Lophura edwardsi and White-winged Duck Cairina scutulata are known to occur at at least three IBAs, although some of these IBAs are not confirmed to regularly support significant numbers. None of the three globally critical and endangered species not |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| confirmed to regularly occur in significant numbers at any IBA (Slender-billed Vulture Gyps tenuirostris, Scaly-sided Merganser Mergus squamatus and Greater Adjutant Leptoptilos dubius) are likely to regularly occur in significant numbers at any site in Vietnam. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[ Back
to index | Next ] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||